|
PHOSPHOROUS ACID | ||
|
PRODUCT IDENTIFICATION |
||
|
CAS NO. |
13598-36-2 |
|
| EINECS NO. | 237-066-7 | |
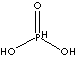
| FORMULA |
(HO)2HPO |
|
| MOL WT. | 82.00 | |
|
HS CODE |
2811.19.6090 | |
|
TOXICITY |
Oral, rat LD50: 1895 mg/kg | |
|
SYNONYMS |
Orthophosphorous acid; Dihydroxyphosphine oxide; | |
|
Phosphorus; Trihydroxide; Trihydroxyphosphine; Phosphonsäure (Dutch); ácido fosfónico (Spanish); Acide phosphonique (French); |
||
| SMILES | OP(O)=O | |
|
CLASSIFICATION |
Phosphorus oxoacid | |
|
EXTRA NOTES |
Phosphorous acid is the compound described by the formula H3PO3. This acid is diprotic (readily ionizes two protons), not triprotic as might be suggested by this formula. Phosphorous acid is an intermediate in the preparation of other phosphorus compounds.(wikipedia) | |
|
PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL PROPERTIES | ||
|
PHYSICAL STATE |
Clear to yellowish Crystal |
|
| MELTING POINT |
73 C |
|
| BOILING POINT | 200 C (Decomposes) | |
| SPECIFIC GRAVITY | 1.651 | |
| SOLUBILITY | 310 g/100ml | |
| pH | ||
| VAPOR DENSITY | ||
|
AUTOIGNITION |
|
|
|
NFPA RATINGS |
Health hazard: 3, Fire: 0, Reactivity Hazard: 1 |
|
|
REFRACTIVE INDEX |
|
|
| FLASH POINT |
| |
| STABILITY | Has not been fully evaluated. Hygroscopic, air sensitive. | |
|
EXTERNAL LINKS & GENERAL DESCRIPTION | ||
| USA.gov - Phosphorous acid Wikipedia Linking - Phosphorous acid Google Scholar Search - Phosphorous acid U.S. National Library of Medicine - Phosphorous acid PubChem Compound Summary - Phosphorous acid KEGG (Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes) - Phosphorous acid http://www.ebi.ac.uk/chebi/ - Phosphorous acid http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/ - Phosphorous acid Material Safety Data Sheet - Phosphorous acid Hazardous Substances Data Bank - Phosphorous acid EPA - Substance Registry Services - Phosphorous acid Local: Applications: Raw material to prepare phosphites; stabilizers for plastics; Water treatment; Bleaching and Cleaning industry; Chemical manufacturing DESCRIPTION OF PHOSPHORUS: Phosphorus is a nonmetallic chemical element in group 15 (nitrogen family, formerly Va) of periodic table; atomic number 15 atomic mass 30.9738; melting point ca 44.1 C (white); boiling point ca 280 C (white); specific gravity 1.82 (white), 2.34 (red), 2.70 (black); valence -3, +3, or +5 ; electronic config. 2-8-5 or 1s 22s 22p 63s 23p 3. The phosphorus molecule is composed of four phosphorus atoms, P4. Phosphorus exists in a number of allotropic forms [white (alpha and beta), red, black and/or violet] in the same physical state. White phosphorus is a white to yellow waxy substance which ignites spontaneously in air to form white fumes of phosphorus pentoxide and glows without emitting heat. Phosphorus is stored underwater as it is extremely poisonous, insoluble in water (but soluble in carbon disulfide). Commercial production of elemental phosphorus is prepared from phosphorite or phosphate rock (apatite, an impure calcium phosphate mineral) reacting with coke and sand or silica pebblesor at high temperatures in an electric furnace. Calcium silicate is produced as a by-product. White phosphorus is used as a deoxidizing agent in the preparation of steel and phosphor bronze. It is also used in rat poisons and to make smoke screens (by burning) for warfare. When white phosphorus is heated to about 250 C with air absence, it changes into the red phosphorus. Red phosphorus, a dark redish powder or crystal, does not ignite spontaneously unless heated to 200 C, does not phosphoresce and it is a little less dangerous than white phosphorus. It is used to make matches. Red phosphorus is prepared commercially by heating calcium phosphate with sand and coke in an electric furnace. Black allotrope is obtained industrially by heating at 300 C under pressure with a mercury catalyst. It has a layer structure and is stable. The major use of phosphorus compounds is in fertilizers, mainly as a mixture called superphosphate (calcium hydrogen phosphate), obtained from phosphate minerals by sulfuric acid treatment; and in nitrophosphates. Phosphorus is burned to make phosphorus pentoxide [phosphorus(V) oxide], a white solid used as a chlorinating agent in organic chemistry, as a drying agent and mainly converted to phosphoric acid used to make phosphates for fertilizers, electro chemical polishing and shaping, electroplating, metal cleaning and pickling in metal treatment by reaction with water. Phosphorus is highly reactive. A wide range of compounds is formed for uses in detergents, water softeners, pharmaceuticals, dentifrices, and in many other important applications. It forms metal phosphides and covalently bonded phosphorus(III) and phosphorus(V) compounds. Phosphoric acid can combine with certain alkaline elements to form salts called phosphates. | ||
| SALES SPECIFICATION | ||
|
APPEARANCE |
Clearto yellowish Crystal | |
|
PHOSPHOROUS ACID |
98.5% min | |
|
PHOSPHATE |
0.2% max |
|
|
CHLORIDE |
0.015% max |
|
|
SULFATE |
0.008% max |
|
|
HEAVY METALS |
15ppm max |
|
|
IRON |
15ppm max |
|
| TRANSPORTATION | ||
| PACKING | ||
| HAZARD CLASS | 8 (Packing group) | |
| UN NO. | 2834 | |
| SAFETY INFORMATION | ||
|
HAZARD OVERVIEW |
GHS (Globally Harmonised System) Classification: Acute toxicity (Oral), Skin irritation, Serious eye damage, Acute aquatic toxicity. Hazard statements: Harmful if swallowed. Causes severe skin burns and eye damage. Potential Health Effects; Eyes - Causes eye burns. Causes severe eye burns. Skin - Harmful if absorbed through skin. Causes skin burns. Ingestion - Harmful if swallowed. Inhalation - May be harmful if inhaled. Material is extremely destructive to the tissue of the mucous membranes and upper respiratory tract. | |
|
GHS |
|
|
| SIGNAL WORD |
Danger |
|
|
PICTOGRAMS |
|
|
|
HAZARD STATEMENTS |
H302-H314 |
|
|
P STATEMENTS |
P273-P305 + P351 + P338 | |
| EC DIRECTIVES |
|
|
| HAZARD CODES |
|
|
|
RISK PHRASES |
22-35 |
|
|
SAFETY PHRASES |
26-36/37/39-45 |
|